
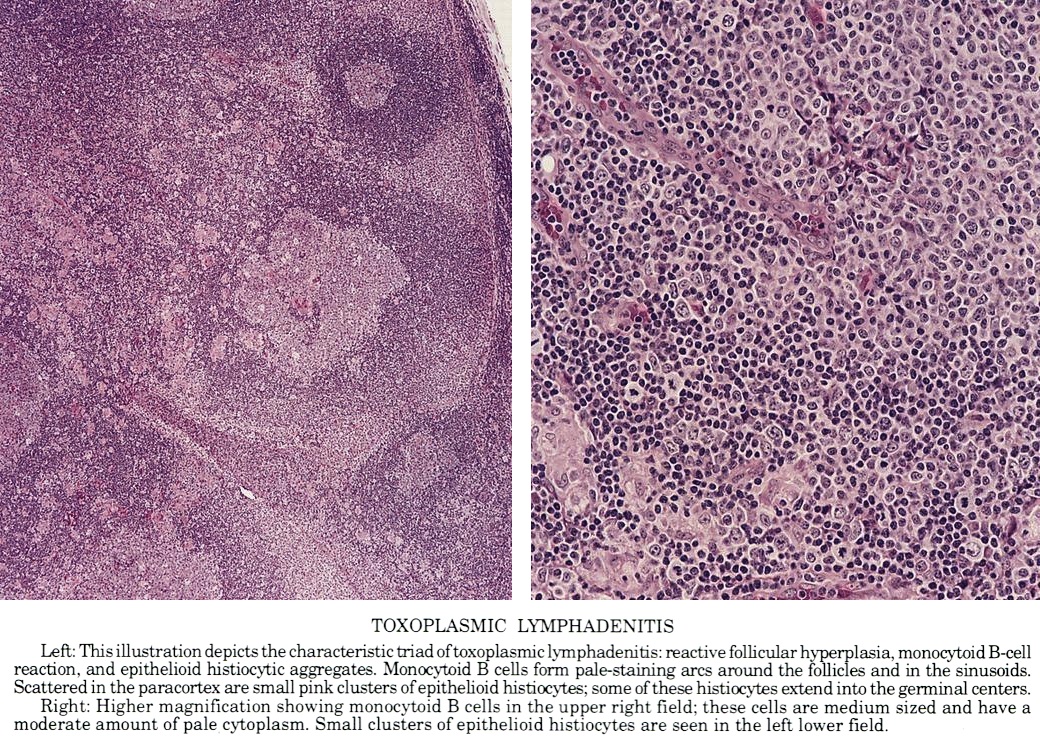
PLD occurs in combination with two forms of Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) - Autosomal Dominant PKD (ADPKD) and Autosomal Recessive PKD (ARPKD) as. In both cases, complications from liver disease can be reduced. polycystic kidney disease pathology outlines. The process of hepatic cytogenesis for these two diseases is caused by defects in remodelling of the ductal plate during biliary tract development, which is called ductal plate. Chronic pyelonephritis - commonly associated with ESRD. Polycystic liver disease (PLD), a genetic cholangiociliopathy, is characterized by the presence of multiple liver cysts of different shape and size filled with cystic fluid. Ex- cept simple hepatic cysts and polycystic liver disease, which can be confidently diagnosed on the basis of ultrasound only, contrast-en- hanced CT or MRI is essential to establish a definitive diagnosis or provide a reasonable differential diagnosis. The results showed pVHL expression in 29 (71%) ICCs but in only 3 (5%) PDAs. infant formula recall 2022 polycystic kidney disease pathology. The incidence of this disease was 17 per 10,000 abdominal explorations.
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is a multisystemic and progressive disorder characterized by cyst formation and enlargement in the kidney (see the image below) and other organs (eg, liver, pancreas, spleen). the preferred approach for patients with severely symptomatic polycystic liver disease with preserved liver and renal function is hepatic resection with drainage, partial liver.
#PATHOLOGY OUTLINES SERIES#
This case series outlines a successful outcome using this operative strategy. However, this disease rarely manifests itself before middle age. PKD also can cause other complications, or problems, such as high blood pressure, cysts in the liver, and problems with blood vessels in your brain and heart.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
